Table of Contents
Vue and React are two of the progressive frontend development frameworks. However, when it comes to choosing between Vue vs React, most teams struggle. The reason is simple. Both frameworks offer capabilities to build apps with a rich user interface. If you look at the numbers, React has an edge: 5x more JavaScript websites than Vue.
However, Vue offers a more integrated solution with built-in tools. So, which one should you choose? This article provides a clear distinction between Vue and React to help you make better decisions for your projects. Let’s start by understanding each framework in the Vue vs React comparison individually.
Vue vs React: An Overview
Here is a comparison of Vue vs React.
You have an overview of the difference between VueJS and ReactJS. Now it’s time to understand each of them individually.
What is Vue?

Vue is a lightweight JavaScript framework that provides advanced web development tools for building modern single-page applications. It is one of the most versatile and progressive frameworks, allowing you to create app code without developing any core features. This means you can make a progressive UI. Plus, it supports high decoupling, enabling you to extend a web app’s functionality with customized modules and visual components.
Leveraging the VueJS development, you can create,
- PWAs and SPAs
- Large-scale enterprise apps
- Extend the existing app function
For any CTO, Vue offers the following differentiators compared to React,
- You can use Vue as a jQuery replacement without rewriting the whole system.
- You can scale up Vue to handle complex single-page applications by leveraging its advanced build chain and ecosystem.
Market Usage And Adoption of VueJS
- Market Share: Vue powers approximately 19.2% of the frontend framework market, with usage on over 3.5 million websites globally.
- Developer Retention: The State of Vue 2025 report indicates extremely high satisfaction, with 93.4% of developers stating they would use it again.
- Downloads: It averages 6.4 million weekly downloads on NPM.
- Enterprise Validation: It is currently used in production by industry giants, proving its stability for large-scale workloads:
- Netflix (internal dashboards/tools)
- Apple (various web properties)
- Nintendo (loyalty programs/sites)
- GitLab (entire frontend is Vue-based)
- BMW, Adobe, and UpWork
What is React?

React is an open-source JavaScript library for building user interfaces, originally developed and maintained by Meta (Facebook). It uses a component-based architecture and a virtual DOM to update and render UI elements efficiently.
This modular design makes React extremely flexible and performant, ideal for modern dynamic web apps. The library focuses on declarative rendering: you describe what the UI should look like, and React updates the DOM as the underlying data changes.
This results in fast, responsive interfaces suitable for complex, data-driven applications.
Leveraging React development, you can create:
- Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) and Single-Page Applications (SPAs): React’s virtual DOM and client-side routing make it easy to build fast, interactive SPAs and mobile-friendly PWAs.
- Large-scale enterprise applications: With frameworks like Next.js and robust state management libraries, React scales to support complex, enterprise-grade web platforms.
- Enhance existing apps: React can be introduced incrementally (e.g., by rendering individual components on a page), enabling you to modernize parts of a legacy application without a complete rewrite.
For any CTO, React offers the following differentiators compared to Vue (and other frameworks):
- Massive ecosystem and corporate backing: React is supported by Meta and a vast ecosystem of tools and libraries (such as Next.js for server-side rendering, Gatsby for static sites, and React Native for mobile). This robust ecosystem means solutions exist for nearly every use case and ensures ongoing innovation.
- Broad industry adoption and talent pool: React is the de facto choice for many companies, so there is a large community and job market. This makes it easier to hire experienced developers and leverage community-built components. It’s a one-way data flow, and virtual DOM also gives predictable performance under heavy load, which is attractive for large applications.
Market Usage And Adoption of React
- Market Share: React is the clear leader among front-end frameworks. On the web, React is used by about 6–7% of all websites (and 7.7% of sites that use any known JavaScript library), making it one of the most widely deployed JavaScript libraries today.
- Developer Adoption: Surveys consistently rank React as the most popular and in-demand frontend framework.
- Downloads: React is widely used on package registries. Its core npm package receives over 20 million downloads per week.
- Enterprise Validation: React’s stability and scalability are proven by its use in production at many global companies. Industry leaders leveraging React include:
-
- Meta Platforms (Facebook, Instagram)
- Netflix
- Airbnb
- Uber
- Dropbox
- Atlassian’s Jira/Confluence
- Salesforce’s Lightning
Now that you know what Vue and React are individually, let’s understand the core differences between them in detail.
Understanding the Core Architecture Difference: Vue vs React
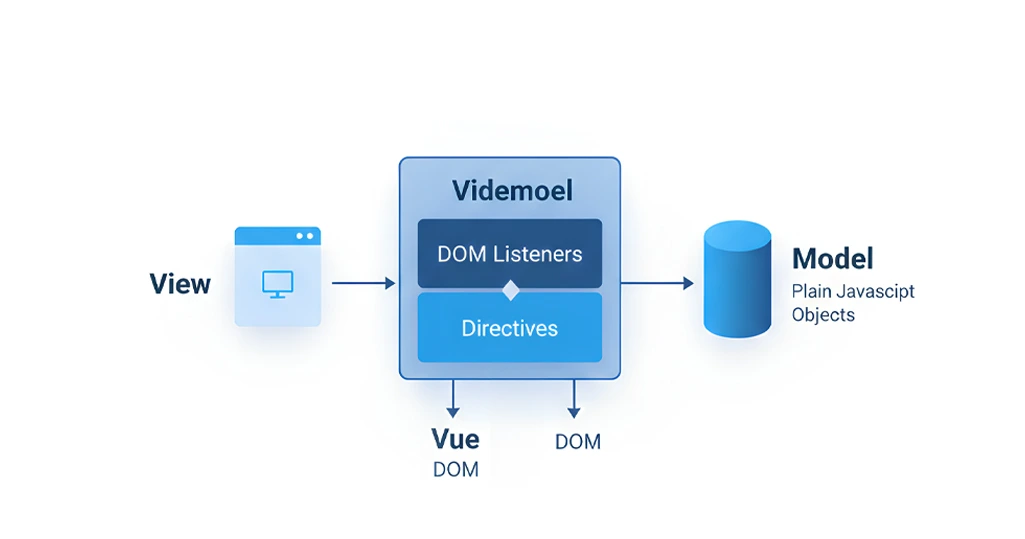
Vue and React both follow a component-based approach. However, the core difference lies in how they structure, compile, and manage the UI layer. Let’s understand these architectural differences between VueJS vs ReactJS.
1. Library vs Framework
When you compare Vue vs React, you are comparing a framework with a JavaScript library. This differentiation is clearly evident in the core of how each handles routing and state management.
React: Library-First Architecture
React is intentionally minimal. It focuses solely on the view layer, relying on external libraries for routing, state management, and advanced tooling. This gives React a flexible, modular architecture, allowing teams to choose their own stack based on complexity, performance needs, and existing infrastructure.
This is why React is ideal for organizations that want maximum control over their architecture and for those scaling into highly customized or distributed systems.
Vue: Framework-Like Architecture
Vue positions itself between a framework and a library. It includes built-in directives, transitions, reactivity, and templating out of the box, enabling faster onboarding and rapid MVP development through a batteries-included architecture.
2. Templating and Rendering Mechanism
When comparing Vue vs React, their most significant architectural difference appears in how each framework handles templating and rendering.
React: JSX Rendering
React renders UI using JSX, where markup lives inside JavaScript. This encourages a JavaScript-first mindset, giving developers complete programmatic control over rendering logic.
Effect on Architecture:
- Unified logic + UI in one place
- Easier dynamic rendering
- More predictable component behavior
Vue: HTML Templates + Optional JSX
Vue uses single-file components (.vue) where HTML, CSS, and JS live in isolated blocks. Templates are declarative and familiar to developers coming from traditional frontend backgrounds.
Effect on Architecture:
- Quicker adoption for teams transitioning from Angular/jQuery
- Clear separation of concerns
- Template compilation optimizes rendering
3. State Management Core
State management is one of the most defining architectural differences in the Vue vs React debate.
React: Explicit State + Immutable Updates.
React architecture revolves around immutable data structures, hooks, and predictable state transitions. It requires manual handling of re-render triggers via hooks such as useState, useReducer, and useMemo.
Enterprise Impact:
- Predictability at scale
- Highly testable pure functions
- More control but more boilerplate
Vue: Automatic Reactivity System
Vue uses a proxy-based reactivity engine that automatically tracks dependencies and updates the DOM when state changes.
Enterprise Impact:
- Less boilerplate and fewer bugs
- Smoother learning curve
4. Virtual DOM Implementation
When evaluating Vue vs React, their Virtual DOM strategies significantly influence performance characteristics.
React: Full Virtual DOM Reconciliation
React re-renders entire component trees when state changes, then efficiently diffs updates using the Virtual DOM.
Strengths:
- Highly predictable under heavy workloads
- Optimized diffing algorithms
- Scales cleanly with complex UI states
Vue: Virtual DOM + Compile-Time Optimization
Vue compiles templates into highly optimized render functions. This allows Vue to skip unnecessary diffs by marking static nodes.
Strengths:
- Faster updates for UI-heavy apps
- Lower memory overhead
- The template compiler gives Vue performance advantages in many scenarios.
5. Component Structure and Scalability
The architectural approach to component design profoundly influences scalability in the Vue vs React comparison.
React: Function-First, Hook-Driven Architecture
React’s modern architecture is built on:
- Functional components
- Hooks
- Context + external state solutions
This creates a pure, composable architecture that is highly flexible for large teams.
Vue: SFCs (Single File Components) + Composition API
Vue offers both:
- Options API (beginner-friendly)
- Composition API (React-like functional logic organization)
For scaling, Composition API brings Vue close to React in terms of flexibility and modularity.
6. Ecosystem and Build Pipeline
The Vue vs React ecosystem comparison highlights two fundamentally different philosophies.
React: Ecosystem-Driven Architecture
React depends on:
- Next.js for SSR/SSG
- Redux/MobX/Zustand/Jotai for state
- React Router for navigation
This gives organizations freedom to design custom architectures, especially for enterprise platforms.
Vue: Integrated, Cohesive Ecosystem
Vue’s official ecosystem includes:
- Vue Router
- Pinia/Vuex
- Vite (default build tool)
This creates a consistent, opinionated development environment with fewer architectural decisions.
An In-Depth Comparison Of Vue vs React
Comparing Vue vs React based solely on technical aspects is not enough. You need to analyze the performance of both React and Vue, flexibility, scalability, and community support.
Vue vs React- Which One Performs Better?
If you compare Vue.js vs React.js in terms of performance, Vue edges over React. Due to its lightweight attribute, Vue makes it faster. However, React also offers faster performance, ensuring improved user experience. With ReactJS development, you can build faster-loading single-page apps.
Reduced DOM manipulation in React speeds up page load time. But what makes Vue more efficient is the lazy loading and virtual DOM. Plus, Vue manages third-party libraries asynchronously. This ensures automatic handling of critical dependencies. It helps you identify the core bundles required.
Which One Is Better For Testing Vue or React?
React comes with test runners, making testing easier. With test runners like Jest and Mocha, you can run tests in standard patterns. This helps testers identify problems in the real browser environments. Plus, it also enables you to find functions that are non-essential and spot any unnecessary execution of expensive functions.
On the other hand, Vue also offers scalable testing abilities. However, the testing in Vue is straightforward. It does not offer any tools but does provide libraries such as Vue Testing Library and Vue Test Utils. One key aspect that makes testing easier in Vue is the feedback loop. With a faster feedback loop, Vue makes code debugging easier.
Vue Or React, Which One Is More Scalable?
React is scalable because it runs on the JavaScript core. You can leverage conventional approaches to organize the React code and scale it easily. At the same time, Vue does offer scalability, but only for smaller applications. However, you can improve its scalability by using Vue Webpacks and multiple Vue features to work around specific coding limitations.
Which Is More Secure?- Vue or React?
When you compare Vue.js vs React.js, Vue offers stronger security with a built-in code sanitizer. React-based apps can be affected by XSS vulnerabilities, server-side rendering attacks, and SQL injections. However, if you can use serialized JavaScript modules, exploit script-injection flaws, and ensure protection of insecure links for better React app security.
Vue vs React: Which Offers Better User Experience?
React offers a better user experience with a rich UI. All the UI components, buttons, forms, text fields, modals, and interactive layouts can be composed, reused, and optimized at scale. Its component-driven architecture ensures UI consistency across complex applications. The React ecosystem also includes design systems like Material UI, Chakra UI, and Ant Design, which accelerate development and improve usability across devices.
Vue, however, delivers a smoother UX for small- to mid-sized interfaces thanks to its lighter footprint and highly intuitive templating system. Its two-way data binding reduces UI inconsistencies and simplifies handling interactive elements. For teams that want rapid prototyping and clean UI logic separation, Vue offers a more beginner-friendly experience without compromising responsiveness.
Vue vs React: Which Has Better Community Support?
React leads with massive community adoption, extensive documentation, and long-term ecosystem stability backed by Meta. Developers get access to thousands of open-source libraries, third-party integrations, plugins, and pre-built components. This broad ecosystem enables teams to resolve edge cases more quickly and streamline development workflows.
Vue also has a strong and rapidly growing community, especially among startups and Asian developer ecosystems. While not as vast as React’s ecosystem, Vue’s maintainers and community contributors release high-quality tools, plugins, and guides. The documentation is highly accessible, making it easy for new developers to onboard. However, for enterprise-scale or ultra-complex projects, React’s community depth still provides more resilience.
Vue vs React: Which Framework Is Better & When to Choose What?
Choosing between Vue and React isn’t just a technical decision—it’s a strategic one. Both frameworks are powerful, production-ready, and trusted by global enterprises. The real question is not “Which is the best?” but “Which one fits your product, team, and long-term roadmap?”
Here’s a clear, decision-focused breakdown to help you evaluate the right fit.
Choose Vue When You Want: Speed, Simplicity & Rapid UI Development
Vue is the better choice when your priorities include:
1. Faster Development & Easier Onboarding
Vue’s HTML-based templates, clear separation of concerns, and intuitive reactive system allow teams to get started faster, especially if they’re coming from Angular, jQuery, or traditional frontend workflows.
Best Fit For:
- Startups building MVPs
- Mid-sized apps needing fast iterations
- Teams with mixed experience levels
- UI-heavy applications where speed of prototyping matters
2. More Built-in Features, Less Configuration
- Vue offers an integrated ecosystem:
- Vue Router
- Pinia (or Vuex)
- Vite build tool
- Official form/transition utilities
This baked-in structure reduces architectural decision-making and avoids the dependency sprawl typical in React projects.
Great for teams who want:
- Predictable project scaffolding
- Minimal third-party dependencies
- Cleaner, more standardized codebases
3. Highly Reactive & Lightweight UI
Vue’s compile-time optimizations and dependency tracking often outperform React in UI-heavy or real-time scenarios.
Good for:
- Dashboards
- Analytics tools
- Real-time interfaces
- Animation-heavy apps
4. Incremental Modernization
Vue can be added to an existing codebase without rewriting the entire app, making it ideal for modernizing legacy UIs.
Choose React When You Want: Maximum Flexibility, Ecosystem Power & Enterprise-Grade Scalability
React becomes the better choice when your project requires:
1. Unmatched Ecosystem & Tooling Options
React’s dominance comes from its ecosystem:
- Next.js (SSR + SSG + server components)
- React Native (mobile apps)
- Gatsby, Remix, Expo
- Thousands of UI libraries
This makes React more future-proof for complex use cases.
Best Fit For:
- Enterprises with multi-platform architecture
- Teams adopting microfrontends
- Companies planning for web + mobile with a shared codebase
2. Complex, Large-Scale Applications
React’s unidirectional data flow, hook-driven architecture, and immutability principles enable better control at scale.
Ideal for:
Product lines with hundreds of components
Apps with dynamic, frequently changing states
Distributed teams that need predictable patterns
3. Massive Talent Availability
React has the largest global developer community and job market, making hiring easier and cheaper, which is critical for enterprises scaling teams quickly.
4. Extensive Customization
Because React is a library, not a framework, you get complete freedom to choose routing, state management, and architectural patterns.
Perfect for organizations that want:
Complete control
Mature DevOps and engineering processes
Tailored architectures over standardized ones
Vue vs React: What Should You Choose?
Vue is better if you want simplicity, speed, and a fully integrated system with minimal setup. It shines for small to mid-sized apps, rapid UI development, and teams that value clean, intuitive codebases. React is better if you want flexibility, a deep ecosystem, and long-term enterprise scalability. It excels at large, complex applications that require strict architectural control and a massive talent pool.
Choosing the proper frontend framework is the first step to successful web app development. Because once you choose the framework, you need a strategic approach. And this is where Ace Infoway can help provide end-to-end web app development solutions for your business. Connect now with our experts to build scalable, reliable web apps for your operations.
FAQs
1. What is the key difference between Vue and React?
The key difference lies in their core philosophy.
Vue is a progressive, full-featured framework that comes with essentials like routing, state management, and transitions built-in. React, on the other hand, is a lightweight JavaScript library focused purely on the view layer. With Vue you get an all-in-one, integrated ecosystem; with React you get maximum flexibility by choosing your own tools through third-party libraries.
2. Which is easier to learn, Vue or React?
Vue is easier to learn, especially for beginners or teams coming from HTML/CSS backgrounds. It uses standard HTML templates and has simpler syntax. React has a steeper learning curve because it requires understanding JSX, hooks, and immutability concepts.
3. Which framework performs better, Vue or React?
Both offer strong performance, but Vue often renders slightly faster thanks to its lightweight architecture, compile-time optimizations, and efficient reactivity system. React also performs well with its Virtual DOM, but may require manual optimizations in large, complex apps.
4. Is Vue scalable for large applications?
Yes, Vue is scalable, especially with tools like Vue Router, Pinia, and the Composition API. However, React is generally considered more scalable for enterprise applications due to its vast ecosystem, mature tooling, and predictable one-way data flow.
5. Which is better for building mobile apps, Vue or React?
React has a clear advantage thanks to React Native, which enables teams to build real native mobile apps. Vue does have options like NativeScript-Vue, but the ecosystem is smaller and less widely adopted.