Table of Contents
Mobile users expect applications that deliver seamless performance across every device, operating system, and network condition. As the mobile ecosystem becomes increasingly fragmented and security risks continue to rise rigorous mobile app testing has shifted from a best practice to a business necessity.
Data shows that growing customer frustration with technology can drive a 45% spike in negative weekly evaluations. In practical terms, every crash, slowdown, or compatibility issue directly impacts user perception, retention, and revenue.
Yet many teams invest heavily in testing without the right tools and checklists, leading to higher costs and limited insights. Even if you decide to plan the entire mobile app testing process, there are queries like,
- Which mobile app testing tools should you prioritize in 2026?
- What capabilities matter most?
- What does a complete, actionable testing checklist look like?
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of mobile app testing, its benefits, a checklist, and the best tools you can use. Developed by our experts, it outlines the essential tests to run, the platforms to consider, and the features that drive measurable quality improvements.
Let’s begin with the fundamentals of mobile app testing.
What is Mobile App Testing?
Mobile app testing is the process of validating whether a mobile application, whether it is for Android or iOS, functions according to predefined metrics and is usable. Testing a mobile application helps verify that the app’s code is working correctly, it’s functioning as expected, and users can efficiently utilize the built-in features.
To ensure successful mobile app testing, teams must test applications across various screen resolutions, operating system versions, and network bandwidths.
Testing a mobile app includes,
- Testing the performance of the application across different OS versions like Android 11.0,12.0, and more.
- Testing the view of an app across device screens, in landscape and portrait modes.
- Validating the compatibility of apps across mobile features, sensors, and hardware.
- Testing the application’s graphical user interface to ensure smoother navigation.
Now that you know what mobile app testing is, here is why you need mobile app testing in 2026
Why Mobile App Testing is Non-Negotiable in 2026?
Mobile apps are complex and require extensive testing to ensure they function correctly. But this is just the tip of the iceberg. The depth of your mobile app testing determines how many improvements you can make to the user experience.
But is it so important?
Let’s understand some core business reasons to test a mobile app,
- User retention and satisfaction – In today’s fast-paced market, users have zero tolerance for app freezes and technical glitches. If your app is buggy or fails to perform as expected, it can lose daily active users. In fact, app crashes are the root cause of 71% of uninstallations.
- Brand reputation and revenue – App crashes, slower performance, and security issues can lead to negative reviews and negatively impact brand reputation.
- Higher maintenance costs – Identifying issues and fixes early is essential to reducing long-term maintenance costs for applications.
- OS fragmentation – With billions of mobile devices and the continuous launch of new models, along with the OS updates from Google Play and Apple App Store. Testing your app on all devices, models, and OS versions becomes crucial.
- Security needs – Increased cyber threats and strict data protection regulations are making security testing increasingly crucial. Especially as rules like GDPR and CCPA change, testing for compliance will become increasingly important.
- AI/ML integrations – With the rise of artificial intelligence and other innovative technologies, it is essential to test mobile applications to determine whether they can effectively integrate AI and related technologies.
What Are The Key Benefits of Comprehensive Mobile Testing?
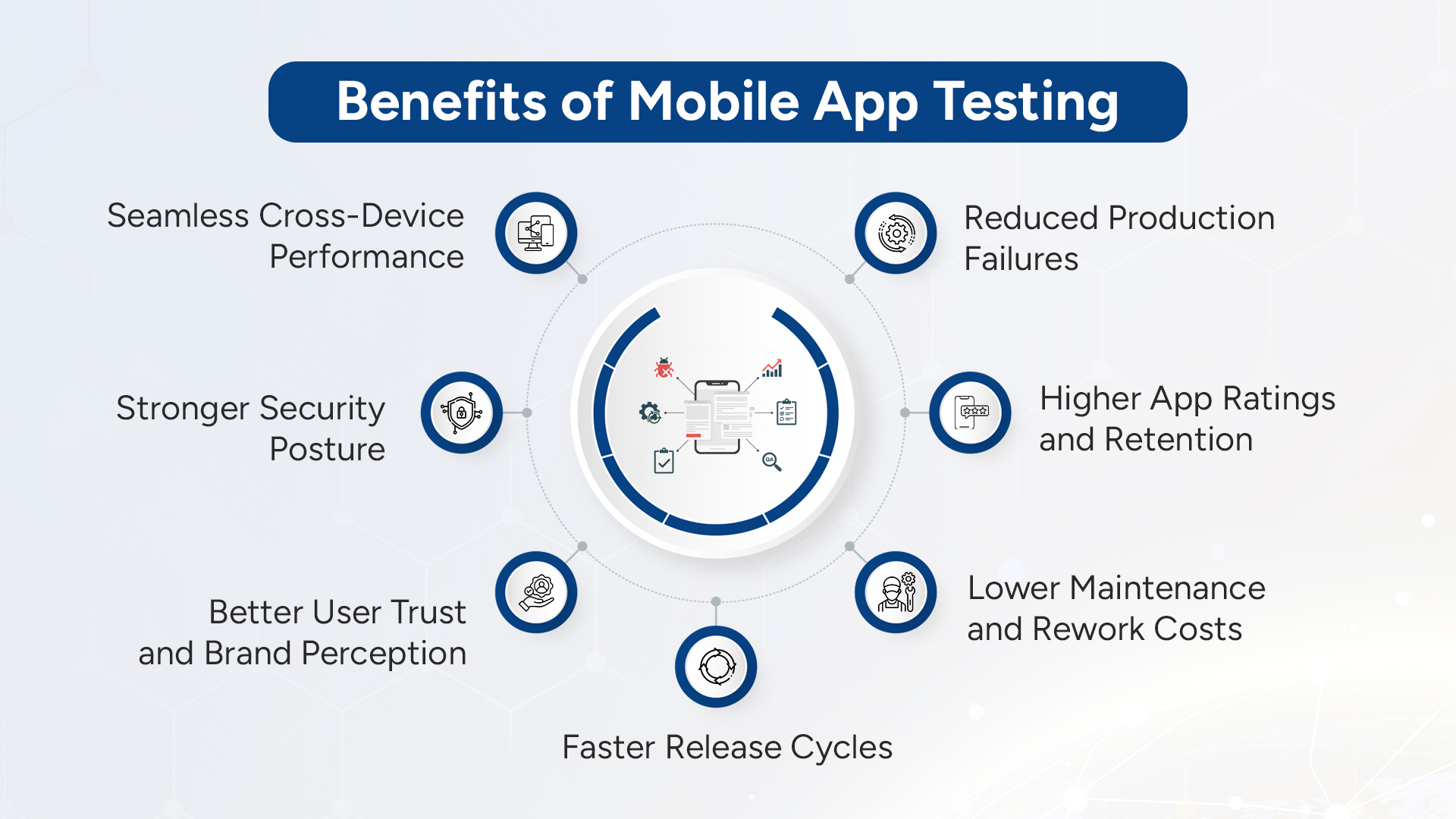
Comprehensive mobile testing provides several key benefits for businesses, including improved app performance, enhanced user satisfaction, and increased cost efficiency. By investing in rigorous testing throughout development, organizations can unlock these advantages and set their apps up for long-term success.
Higher App Ratings and Retention
Thorough mobile app testing ensures that bugs, usability issues, and performance problems are identified and resolved before launch, resulting in smoother and more reliable user experiences. This leads to higher user satisfaction, positive app store reviews, and increased retention rates, as users are less likely to uninstall well-performing apps.
Lower Maintenance and Rework Costs
Early and comprehensive testing helps detect bugs and errors before they reach production, significantly reducing post-launch maintenance and rework costs. Addressing issues during development is more cost-effective than fixing them after release, as it saves both time and resources for businesses.
Faster Release Cycles
Automated testing and agile-friendly QA processes enable rapid feedback loops, allowing development teams to identify, fix, and deploy changes quickly and efficiently. Integrating QA within CI/CD pipelines further accelerates release cycles, enabling businesses to bring features and updates to market faster.
Better User Trust and Brand Perception
A stable, polished mobile app reflects positively on a brand’s professionalism and reliability. Consistently good app performance and user experience foster greater user trust, prevent negative feedback, and maintain a positive brand image, crucial for long-term business success.
Stronger Security Posture
Comprehensive security testing is vital for identifying vulnerabilities and safeguarding user data. Identifying and resolving security issues promptly helps protect sensitive information, mitigates regulatory and financial risks, and enhances the app’s overall security posture.
Seamless Cross-Device Performance
Testing across a variety of devices, OS versions, and network conditions ensures compatibility and functionality regardless of user environment. This maximizes market reach and prevents device-specific bugs from affecting the user experience, further reducing the risk of negative reviews or customer churn.
Reduced Production Failures & Accelerated Product-Market Fit
Comprehensive mobile testing minimizes the likelihood of unexpected failures or downtime in production. Reliable, bug-free releases create a smoother path to product-market fit, as users encounter fewer obstacles and are more likely to adopt and recommend the app.
Your Essential Mobile App Testing Checklist: Covering Every Angle
Building a reliable, high-performing mobile app requires a structured mobile app testing checklist backed by the right mobile app testing tools and repeatable processes. Whether you’re performing manual QA or mobile app automation testing, each testing layer ensures your product works flawlessly across devices, networks, and real-world user scenarios.
1. Functional Testing
Functional testing ensures your mobile app’s core features work consistently and accurately across all user journeys. This step in your mobile app testing process verifies that every flow from login to checkout behaves as expected under normal and edge-case conditions.
Navigation and user flows – You walk through key journeys (signup, login, search, checkout, profile update) to ensure every screen transition, button, and link leads to the right place without dead ends or loops.
Input actions and form validation – You try valid and invalid inputs (empty fields, wrong formats, long text, special characters) to confirm the app shows the correct errors and never crashes or accepts insufficient data.
API communication – You verify that the app sends correct requests, handles slow/failed responses gracefully, and displays accurate data from the backend without duplicates or corruption.
Offline and online states – You cut and restore the network, use airplane mode, and experience weak connections to verify that the app caches data correctly, syncs cleanly, and doesn’t lose user work.
Error handling – You deliberately trigger errors (bad credentials, timeouts, invalid actions) and check whether the app shows clear, actionable messages and safe fallbacks instead of generic failures.
Push notifications – You confirm that messages are received at the right time, that deep links open the correct screen, and that opt-in/opt-out preferences are respected across sessions.
2. Performance Testing
Performance testing measures how fast, stable, and resource-efficient your app is under various load conditions. As part of your mobile app testing checklist, it helps you identify bottlenecks that impact speed, responsiveness, and overall user experience.
- App launch time – You measure how long it takes from tap to usable screen, aiming to avoid slow starts that cause users to abandon the app.
- Memory consumption – You monitor RAM usage during both typical and heavy use to identify leaks and bloat that can cause freezes or OS-level shutdowns on low-end devices.
- CPU usage – You profile how much processing power the app uses, especially during animations, background tasks, or complex operations, to avoid overheating and lag.
- Battery drain – Run long sessions to see if the app drains battery abnormally, particularly when using GPS, the camera, or making frequent network calls.
- Network performance – You simulate 2G to 5G and poor Wi‑Fi to see how the app behaves with latency, packet loss, and bandwidth constraints.
- Stress and load behavior – You push the app to high concurrent usage, rapid taps, and repeated operations to ensure it remains stable, responsive, and error-free.
3. Usability Testing
Usability testing ensures your mobile app feels intuitive, easy to navigate, and frictionless for real users. It confirms whether users can complete key tasks without confusion, an essential component in any mobile app testing strategy.
- Onboarding clarity – You observe how first-time users move through intro screens, sign-up, and permissions to ensure they understand the value and don’t drop off early.
- Navigation ease – You check if users can find core features without training, and whether menus, tabs, and gestures feel intuitive.
- Visual hierarchy – You verify fonts, colors, spacing, and layout to guide attention to primary actions and information, reducing cognitive load.
- Accessibility – You test large fonts, screen readers, color contrast, and touch target sizes to ensure people with disabilities can still use the app effectively.
- Gesture responsiveness – You ensure scrolling, swiping, pinching, and other gestures respond smoothly and predictably, even on lower-end devices.
- Error message clarity – You review errors and empty states for plain, helpful language that informs users of the issue and provides clear instructions for resolving it.
4. Security Testing
Security testing protects user data, backend systems, and business assets. It ensures your mobile app is safeguarded against vulnerabilities, unauthorized access, and real-world attack patterns critical for compliance and trust.
- Authentication security – You test login, MFA, password reset, lockouts, and brute-force resistance to ensure accounts cannot be easily hijacked.
- Data encryption at rest and in transit – You confirm that sensitive data is encrypted on the device and uses secure protocols (such as HTTPS/TLS) over the network.
- Secure session management – You verify tokens, cookies, and sessions expire correctly, cannot be reused or stolen easily, and are revoked on logout.
- Vulnerable third-party libraries – You scan SDKs and dependencies for known CVEs, misconfigurations, and unsafe default settings.
- API protection and rate limiting – You attempt to abuse patterns (rapid calls, parameter tampering) to ensure the backend enforces authorization and throttling.
- Jailbreak/root detection – You check whether the app can detect high-risk devices and restrict sensitive operations to reduce fraud and tampering risk.
5. Compatibility Testing
Compatibility testing verifies that your app behaves consistently across devices, OS versions, screen sizes, and network types. This helps you reduce fragmentation issues and deliver a uniform user experience across the entire device ecosystem.
- Android and iOS versions – You run the app on supported OS ranges (including at least one older version) to catch OS-specific bugs or deprecated APIs.
- Screen sizes and resolutions – You validate layouts across small and large phones and tablets to ensure the UI doesn’t break, overlap, or clip.
- Chipsets and RAM variations – You test on low-, mid, and high-end hardware to see how performance and stability differ across them.
- OEM UI layers – You check devices from major manufacturers (Samsung, Xiaomi, etc.) whose custom skins can alter behavior or permissions.
- Network types (2G–5G, Wi‑Fi) – You revisit key flows under different network types and strengths to ensure graceful degradation and reliable syncing.
6. Localization Testing
Localization testing ensures your mobile app feels native in every supported language and region. It checks translation accuracy, regional formats, and cultural relevance—ensuring global users enjoy a seamless, localized experience.
- Language correctness – Native or fluent reviewers check translations for meaning, tone, and domain accuracy, not just literal wording.
- UI alignment after translation – You ensure that longer translations do not result in truncated labels, broken buttons, or misaligned layouts.
- Regional formats (date, currency) – You verify dates, times, numbers, currencies, and units follow local conventions everywhere they appear.
- Culturally relevant content – You review images, icons, colors, and phrases to avoid cultural insensitivity or confusing metaphors in each locale.
The above checklist has been prepared by our dedicated development team, which has more than 2 decades of experience delivering mobile app solutions. But this is not all! We have also curated a list of top mobile app testing tools you can use for your projects.
Top Mobile App Testing Tools For 2026
Top mobile app testing tools for 2026 include Appium, LambdaTest, Espresso, and Selenium. These tools offer a range of solutions from open-source, cross-platform automation to cloud-based platforms and platform-specific mobile app development frameworks.
Automation Testing Tools
Automation testing tools are software applications that automate repetitive tasks in software testing, such as simulating user interactions and comparing actual outcomes with expected results to verify an application’s functionality and performance.
1. Appium
Appium is the de facto open-source automation framework for mobile UI testing that drives native, hybrid, and mobile-web apps using the WebDriver protocol. It abstracts away device-specific details so test teams can write platform-agnostic scripts in popular languages (Java, Python, JavaScript, Ruby, C#).
Use Appium when you need cross-platform coverage with a single test suite and want to reuse automation logic across Android and iOS. Appium integrates easily with CI/CD and test runners, and supports advanced gestures, context switching, and parallel execution via Selenium Grid or cloud providers.
Key features
- Cross-platform test execution (Android + iOS).
- Language-agnostic clients (Java, Python, JS, etc.).
- WebDriver protocol compatibility for reuse of existing Selenium skills.
- Supports hybrid app context switching (webview/native).
- Works with device farms and CI systems for parallel runs.
2. Selenium
Selenium is the standard for browser automation and is used for mobile web testing when your app is served in a browser or as a PWA. While it doesn’t natively automate the native app UI, it pairs with Appium so teams can reuse web automation logic for mobile web checks. Choose Selenium when responsive behavior, cross-browser parity, and web UX validation are priorities.
Key features
- Mature browser automation ecosystem (WebDriver).
- Excellent cross-browser and responsive testing capabilities.
- Integrates with CI, test frameworks, and cloud browsers.
- Reuse of browser test suites for mobile-web validations.
3. Espresso (Android)
Espresso is Google’s UI testing framework for Android, built for speed and stability within Android Studio. It runs inside the app process for fast, deterministic tests and integrates tightly with Gradle and Android toolchains.
Se Espresso for white-box UI testing, component interaction tests, and regression checks where speed and reliability are essential. It’s ideal for developer-owned tests and CI pipelines that require quick feedback loops.
Key features
- Very fast, reliable UI tests (runs in app process).
- Tight Android Studio & Gradle integration.
- Synchronization with the UI thread reduces flaky waits.
- Great for unit- and UI-hybrid testing strategies.
4. XCUITest (iOS)
XCUITest is Apple’s native UI automation framework integrated into Xcode. It provides highly stable interaction with iOS UI components, supports XCTest assertions, and runs on simulators and real devices.
Choose XCUITest for iOS regression testing, accessibility verification, and performance-sensitive scenarios where native fidelity is crucial. Tests are typically written in Swift or Objective-C and fit naturally into Xcode CI workflows.
Key features
- Native iOS environment for highly accurate UI checks.
- Integrated with Xcode and XCTest test reporting.
- Low flakiness and fast execution on simulators/devices.
- Suitable for accessibility and UI performance tests.
5. Robot Framework
Robot Framework is a generic, keyword-driven test automation framework that emphasizes readability and maintainability. It’s not mobile-specific but commonly used with Appium and other libraries to build enterprise test suites.
Robot Framework offers a table-like syntax that makes it accessible to non-developers (QA analysts) while supporting Python/Java extensions. Use Robot Framework when you want high-level test cases, clear separation of test data, and modular keywords that scale across teams.
Key features
Keyword-driven, readable test cases for broad team use.
Extensible through libraries (AppiumLibrary, SeleniumLibrary).
Suitable for acceptance testing and business-readable suites.
Support for parallel execution and custom libraries.
Manual & Distribution Tools
Manual mobile app testing tools primarily consist of issue-tracking and test management systems. Distribution testing, on the other hand, focuses on evaluating how your mobile app performs when accessed by users spread across different geographies, devices, networks, and traffic patterns. It simulates real-world distributed load to help identify performance bottlenecks, latency issues, API slowdowns, and backend scalability limitations.
6. TestFlight (iOS)
TestFlight is Apple’s official beta distribution and feedback tool. It streamlines the distribution of pre-release IPA builds to internal and external testers and the collection of crash reports, session logs, and tester feedback. Use TestFlight during alpha/beta cycles to gather real-user telemetry, UX impressions, and bug reports from a controlled audience before App Store release.
Key features
- Simple invite flow for internal/external testers.
- Integrated crash and feedback collection.
- Version management and expiration controls.
- Ideal for staged iOS releases and pre-launch validation.
7. Google Play Console (Testing Tracks)
The Google Play Console offers internal, closed, and open testing tracks, as well as staged rollouts, for Android apps. It centralizes distribution, crash/ANR reports, analytics, and user feedback. Use Play Console for controlled releases, A/B testing of builds, and monitoring real-world crash metrics before wider rollout.
Key features
- Multiple testing tracks and staged rollouts.
- Crash, ANR, and performance reporting (Play Console & Firebase).
- Country and device targeting for releases.
- Beta feedback and pre-launch reports.
8. Emulators & Simulators
Emulators (Android) and simulators (iOS) mimic device hardware and OS behavior and are used for rapid early validation of UI, flows, and functionality. They’re indispensable for development-time debugging, running unit tests, and reproducing many, but not all, device-specific issues. Emulators are fast and repeatable, but always complement them with real-device tests for sensor, network, and performance characteristics.
Key features
- Fast iteration and debugging during development.
- Configurable device specs, locales, and network conditions.
- Cheap and quick for smoke and functional checks.
- Not a substitute for real-device performance and sensor validation.
Distributed Load & Performance Testing Tools
Distributed load testing tools help analyze how your mobile app backend, APIs, and infrastructure behave under global traffic. They simulate thousands of virtual mobile users across regions, networks, and
request patterns, replicating real-world distributed usage.
9. JMeter (Apache JMeter)
JMeter is an open-source load testing tool designed to test server performance and measure API responsiveness under heavy load. It can emulate thousands of concurrent users and supports highly distributed load generation through cloud servers.
Key Features
- API load, stress, and endurance testing
- Distributed test execution via multi-machine clusters
- Plugins for geo-distributed load injection
- Ideal for testing mobile login, search, checkout, and API-heavy workflows
10. Gatling
Gatling is a high-performance load testing tool with a non-blocking architecture that allows simulating very high traffic with minimal infrastructure. Its DSL-based scripting is ideal for teams that want readable, repeatable load test scenarios.
Key Features
- Highly scalable, non-blocking engine
- Developer-friendly DSL for complex test flows
- Built-in HTML reports and performance dashboards
- Excellent for backend/API scalability and stress tests
11. Locust
Locust is a Python-based distributed load-testing tool that makes it easy to simulate millions of concurrent users with simple Python scripts. It scales horizontally across multiple machines, making it ideal for testing real-world distributed use cases.
Key Features
- Python-based scripting for easy scenario creation
- Horizontal scaling across a distributed infrastructure
- Web UI for real-time load monitoring
- Great for simulating real mobile user traffic patterns
Performance Monitoring Tools
Performance monitoring tools track and analyze system and application performance to identify issues, improve efficiency, and ensure optimal user experience. Some of these tools are,
12. Firebase Performance Monitoring
Firebase Performance Monitoring captures app startup time, network request metrics, screen rendering traces, and custom traces across Android and iOS. Its real-user monitoring model surfaces device- and region-specific performance degradations. Use Firebase to quickly identify slow screens, heavy API calls, and post-release regressions with dashboards and integration into the Firebase ecosystem.
Key features
Real-user performance metrics and traces.
Automatic network and app-start instrumentation.
Device/OS-segmented insights and alerts.
Easy integration with Crashlytics and Analytics.
Security Testing Tools
Mobile app security testing tools identify vulnerabilities by analyzing applications for security flaws. Some of the key mobile app security testing tools are,
13. Mobile Security Framework (MobSF)
MobSF is an open-source, automated toolkit for mobile security testing that supports static (SAST), dynamic (DAST), and malware analysis. It analyzes APKs/IPAs, inspects code and manifest issues, flags insecure configurations, and produces actionable reports. Use MobSF early in CI pipelines for automated security gates and during pentests for quick vulnerability scans.
Key features
- Static & dynamic analysis for Android/iOS binaries.
- API & manifest security checks and insecure code patterns.
- Quick vulnerability reports and remediation pointers.
- Integrates into CI for pre-merge security checks.
14. OWASP MASVS (Mobile Application Security Verification Standard)
OWASP MASVS is not a tool but a prescriptive security standard and checklist that outlines required security controls for mobile apps. It helps teams structure threat models, define security goals, and measure compliance. Use MASVS to guide architecture reviews, penetration tests, and to demonstrate adherence to recognized security practices.
Key features
- Structured security requirements for mobile apps.
- Guidance for secure storage, transport, authentication, and runtime.
- Useful for audits, threat modeling, and compliance tracking.
- Often paired with tools like MobSF for verification.
Cloud-Based Mobile App Testing Tools
Cloud-based device and testing labs for mobile apps are remote platforms provided by third parties that allow developers and QA teams to access a wide variety of real and virtual mobile devices on demand.
It enables comprehensive testing across different hardware, operating systems (both iOS and Android), browsers, and network conditions, eliminating the need for organizations to purchase, manage, or maintain an expensive in-house physical device lab.
15. Sauce Labs
Sauce Labs is a comprehensive cloud testing platform that provides automated and live testing for web and mobile applications. It supports parallel execution, visual testing, and analytics, with enterprise features such as single sign-on, compliance controls, and long-term reporting. Use Sauce Labs for scalable enterprise-level automation and shared cross-team device resources.
Key features
- Large device cloud for parallel automated runs.
- Visual testing and video captures for debugging.
- Robust CI integrations and enterprise governance.
- Performance testing add-ons are available.
16. LambdaTest
LambdaTest offers a cost-effective device cloud and automation platform for cross-browser and cross-device testing. It supports Appium and Selenium automation, manual live device testing, and provides debugging artifacts (videos, logs). Use LambdaTest when you need scalable device coverage with straightforward CI integrations and budget considerations.
Key features
- Real device & emulator access with debugging logs.
- Appium and Selenium automation support.
- CI/CD integrations and parallel runs.
- Affordable tiers for small/medium teams.
Final Note
Mobile app testing is the backbone of product success in 2026. It improves performance, strengthens security, enhances user experience, and reduces post-launch failures. Applying a comprehensive mobile app testing checklist, leveraging the right tools, and adopting automation, teams can deliver apps that exceed user expectations.
However, it’s the application of these tools and checklists that matters, and Ace Infoway can help you with customized mobile app testing solutions. With more than 27 years of experience in delivering mobile app development and testing solutions across industries, we have the expertise your project needs.
Are you ready to leverage these mobile app testing tools and checklists to transform the user experience? Then contact us now.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between Appium, Espresso, and XCUITest, and which should I choose?
Use native frameworks (Espresso for Android, XCUITest for iOS) when you need fast, stable tests tightly integrated with the platform; choose Appium when you need a single, cross-platform test suite or your QA staff prefers language-agnostic scripts. Many teams start with Appium for coverage, then adopt native frameworks for speed/low flakiness.
2. Are native frameworks really less flaky and faster than Appium?
Yes, native frameworks run inside the app process and are generally faster and more deterministic. Appium trades some speed and stability for cross-platform convenience. For large, high-frequency CI pipelines, teams often prefer Espresso/XCUITest for reliability.
3. Can I rely only on emulators/simulators for testing?
No. Emulators/simulators are excellent for fast development checks (UI flows, unit tests), but real devices are essential for performance, sensors (GPS/camera), battery, and network behavior. Best practice: emulator-first, then a representative real-device matrix.
4. What’s the minimum device matrix I should test on?
Start with one recent flagship, one popular mid-range, one low-end device, and a tablet (if applicable). Cover at least: current OS, one previous major OS, and any region-specific OEM skins. Communities recommend this mix for cost-effective coverage.
5. How do I pick between cloud device farms (Sauce Labs, LambdaTest, BrowserStack) and building an in-house lab?
Use cloud device farms if you need broad device/OS coverage quickly, parallel runs, and low maintenance. Build an in-house lab only if you need complete physical control, have predictable scale, or stringent data policies. Cloud providers are typically the fastest ROI for most teams.
6. What tests should be automated vs kept manual?
Automate repeatable, high-value flows: smoke tests, critical user journeys, regression suites, and API checks. Keep exploratory testing, visual/UX reviews, accessibility audits, and early usability checks manual. Automation + periodic manual sessions is the winning combo.