Table of Contents
At first glance, ReactJS and React Native seem interchangeable, and that’s exactly where many teams go wrong. While both are built on JavaScript and follow a component-based architecture, they’re designed for fundamentally different platforms and outcomes.
ReactJS is built for the browser, powering fast, interactive web interfaces. React Native, on the other hand, is designed to deliver near-native mobile experiences on iOS and Android using shared code.
The real challenge isn’t understanding these frameworks but choosing the right one for your software development strategy. Too often, teams decide based on familiarity or assumptions, rather than platform needs, user behavior, and long-term scalability.
When comparing ReactJS vs React Native, looking beyond surface-level similarities is critical. If your product is web-first, ReactJS is a natural fit. If your audience is mobile-centric, React Native offers native performance without starting from scratch.
In this blog, we break down what ReactJS and React Native are, how they differ in core features and performance, their advantages and limitations, and the key factors that should guide your decision.
What Is ReactJS?
ReactJS (React) is an open-source JavaScript library for creating user interfaces for web applications. In simple terms, ReactJS helps you build fast, interactive websites that run inside a browser.
Its biggest strength lies in its component-based architecture. Instead of writing massive blocks of UI code, you break your interface into small, reusable components.
Each component manages its own logic and presentation, which keeps your codebase cleaner, easier to maintain, and far more scalable as your product grows. According to Statista, around 44.7% of users used ReactJS in 2025.
ReactJS also introduces JSX, a JavaScript extension that lets you write HTML-like markup directly alongside your JavaScript logic.
Then there’s React’s virtual DOM, a lightweight, in-memory version of the real browser DOM. Rather than updating the entire page whenever something changes, React intelligently calculates the smallest possible update and applies only that change.
ReactJS is lightweight by design, which means you can use it to power an entire single-page application or simply add interactivity to an existing site. This adaptability is one reason companies like Facebook, Instagram, and Netflix rely on ReactJS to deliver responsive user experiences at scale.
If your goal is to build modern web interfaces quickly, consistently, and with long-term maintainability in mind, React fits naturally into that equation.
Advantages of ReactJS
When evaluating React Native and ReactJS, ReactJS clearly shines in browser-based development. Here’s why teams continue to rely on it for scalable web experiences:
- Developer-friendly tools: ReactJS provides built-in debugging utilities that let developers inspect component states and props in real time, speeding troubleshooting and reducing development cycles.
- Simple dynamic interfaces: By minimizing boilerplate and emphasizing reusable components, ReactJS makes it easier to build interactive web applications without repetitive coding patterns.
- Optimized rendering with Virtual DOM: ReactJS stores UI updates in memory before syncing them with the real DOM, resulting in smoother interactions, faster rendering, and improved overall performance.
- Modular architecture: Applications are built using self-contained components, enabling code reuse, simplifying maintenance, and supporting long-term scalability as projects grow.
If you’re planning to build scalable web interfaces using ReactJS, exploring professional ReactJS development services can help you accelerate delivery while ensuring performance and maintainability.
What Is React Native?
React Native takes the same core React concepts and applies them to mobile app development.
Instead of targeting browsers, React Native lets you build applications for iOS, Android, and even Windows, using your existing React knowledge. That’s a game-changer for teams that want to move fast across platforms without maintaining separate codebases for each one.
With React Native, much of your business logic can be shared between web and mobile projects. This dramatically reduces development time and ensures consistent behavior across platforms.
But here’s the key difference: React Native doesn’t render HTML. Instead of working with the virtual DOM, it uses native components provided by each platform, such as buttons, lists, views, panels, and more.
These components map directly to their platform equivalents, which means your apps look, feel, and perform like they were built specifically for iOS or Android.
Animations are smoother. Gestures feel natural. UI elements automatically follow the host operating system’s design guidelines.
That’s why companies like Discord, Uber, and Skype use React Native to power their mobile experiences because it delivers native performance while preserving the efficiency of React-based development.
Advantages of React Native
While ReactJS focuses on the web, React Native extends the same development philosophy to mobile platforms, making it a powerful companion in the react native andReactJSS ecosystem:
- JavaScript-based development: Developers can use their existing JavaScript and React knowledge to start building native mobile apps, reducing onboarding time and accelerating delivery.
- Single shared codebase: React Native enables teams to build iOS and Android apps from a single codebase, reducing development effort while maintaining consistency across platforms.
- Hot reloading: Code changes appear instantly in the running app, enabling faster iteration, easier debugging, and a more efficient development workflow.
- Native UI components: React Native uses platform-specific components to ensure apps look and behave like actual native experiences, even when platform-level customization is required.w
- Continuous ecosystem improvements: Backed by a strong community, React Native constantly evolves to support the latest iOS and Android features, helping teams stay future-ready.
ReactJS vs React Native: Key Feature Differences That Actually Matter
Choosing between React Native and React JS isn’t about which framework is trendier. It’s about understanding how each one fits your product goals.
Both share JavaScript. Both rely on components. But the difference between React and React Native becomes evident once you compare how they handle web and mobile experiences.
Let’s simplify the ReactJS vs React Native conversation by looking at what each does best.
Core Features of ReactJS
ReactJS is explicitly built for browser-based experiences. Its feature set makes it ideal for modern, interactive web platforms:
- Single-Page Applications (SPAs): ReactJS dynamically updates content without refreshing the page, making apps faster and more responsive and making them perfect for platforms like dashboards, portals, and SaaS products.
- Complex UI management: Its component-based architecture allows developers to break large interfaces into reusable parts, simplifying maintenance and scaling.
- Real-time dashboards and data visualization: ReactJS efficiently refreshes UI elements as data changes, making it suitable for analytics tools and monitoring systems.
- Social media functionality: Handles live notifications, feeds, and comments smoothly using optimized rendering.
- Custom widgets and components: Enables creation of tailored UI elements when standard libraries fall short.
- eCommerce and eLearning platforms: Supports dynamic product catalogs, shopping carts, interactive lessons, and personalized content delivery.
How ReactJS Works?
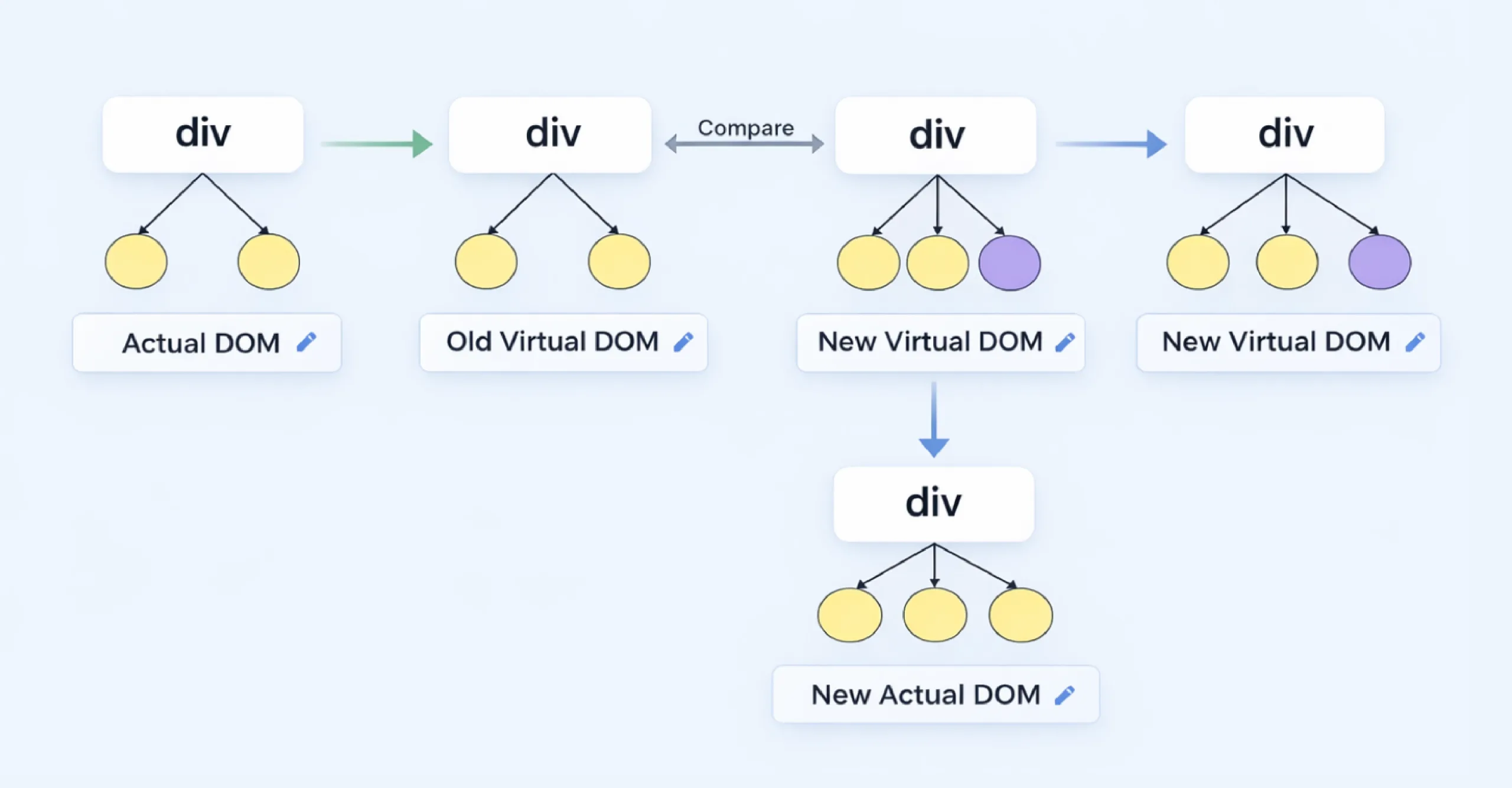
ReactJS organizes applications into independent UI components. Each component manages its own state.
When something changes, ReactJS updates the virtual DOM first. It then compares that with the previous version and applies only the necessary updates to the real DOM.
This selective rendering is what keeps ReactJS fast.
Within the React Native and ReactJS ecosystem, this highlights a significant difference between React and React Native: ReactJS optimizes browser performance, making it ideal for modern web apps.
Core Features of React Native
React Native enables true native apps with shared JavaScript logic, making it a key player in the React Native and ReactJS ecosystem when it comes to mobile app development:
- Cross-platform development: Build iOS and Android apps from a single codebase, reducing development time and cost.
- Rapid prototyping: Quickly validate app ideas across platforms before investing in full-scale development.
- Ideal for limited resources: Allows small teams to reach mobile users without maintaining separate Android and iOS projects.
- IoT and home automation support: Powers mobile interfaces for smart devices, remote monitoring, and connected environments.
- Content-driven applications: Well-suited for news apps, blogs, and media platforms with consistent UI across devices.
- Expandable native apps: Can be integrated into existing mobile applications to add reusable components and new features.
This is where the distinction between ReactJS and React Native becomes clear: React Native focuses on native mobile experiences, while ReactJS dominates the web.
How React Native Works?
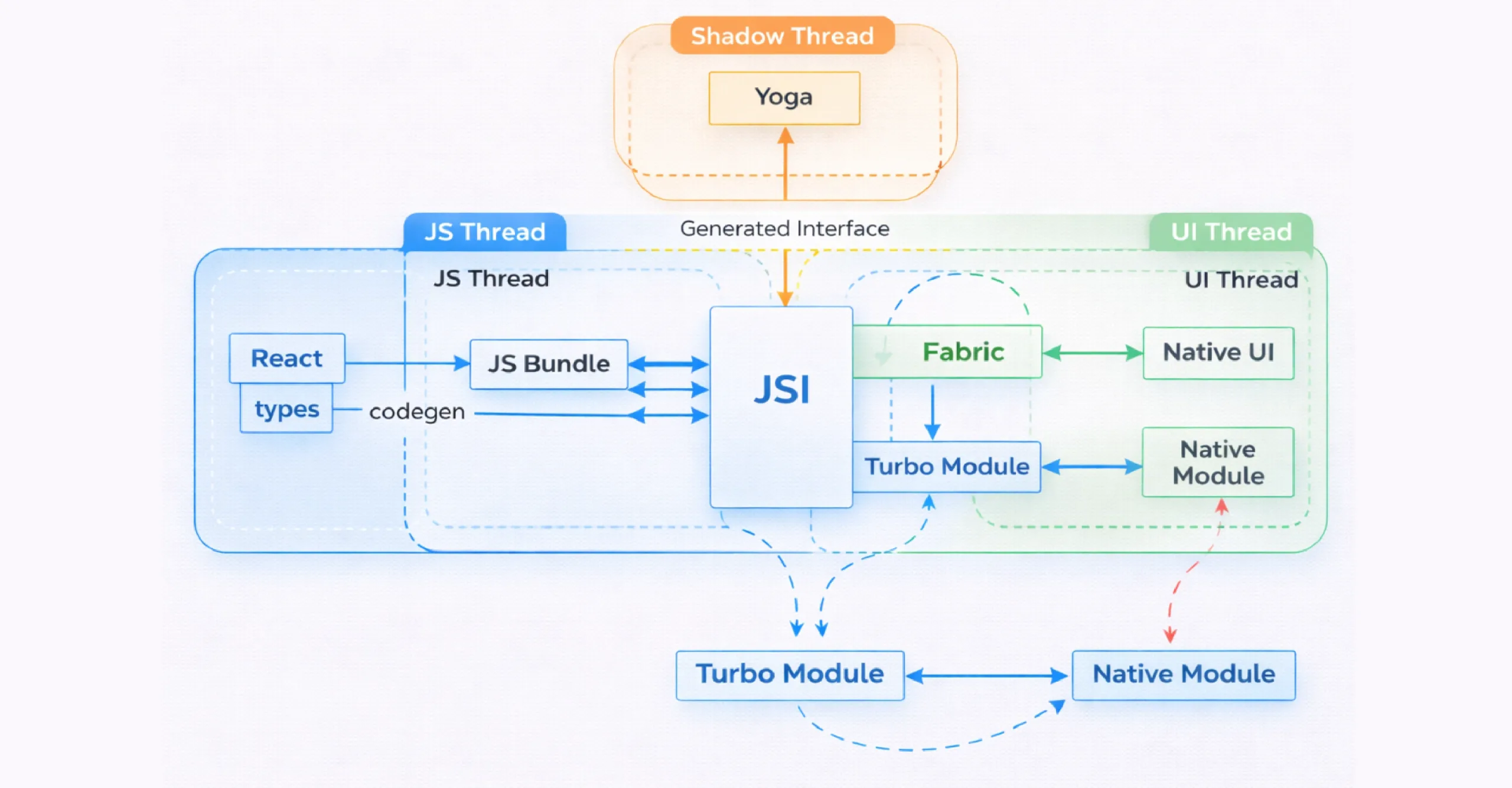
Unlike ReactJS, React Native doesn’t use the browser DOM. Instead, it runs logic on a JavaScript thread and renders UI on a Native thread. Data flows between them to create truly native interfaces.
Earlier versions relied on a bridge that caused performance overhead. Today’s architecture replaces that with Turbo Modules, Fabric, and Codegen, removing bottlenecks and improving responsiveness.
We recently applied this same architecture while working on a Re-development Web Portal and Mobile Applications project, modernizing legacy systems and delivering seamless cross-platform experiences.
How to Choose Between ReactJS and React Native?
If you’re stuck between React Native and ReactJS, you’re not alone. This is one of the most common questions teams face when planning a modern application.
On the surface, both look similar. They share JavaScript. They follow the same component-based mindset. But when you face real-world requirements, the ReactJS vs React Native decision becomes much clearer and deeper.
Here are the key factors that should guide your choice.
1. Platform: Web or Mobile Comes First
Start with the obvious.
ReactJS is built for web applications that run inside browsers.
React Native is designed for native mobile apps on iOS and Android.
If your product lives on the web, ReactJS is the natural fit. If your users primarily interact on smartphones, React Native is the better option. This single distinction often settles most ReactJS vs React Native debates right away.
2. Target Audience and Use Case
Next, think about where your users spend their time.
If your audience is desktop-heavy, which includes corporate dashboards, SaaS platforms, and internal tools, then ReactJS makes sense. But if your users are mobile-first, React Native lets you deliver native mobile experiences with smooth gestures, animations, and platform-specific UI.
Understanding your audience behavior is critical when choosing between React Native and ReactJS.
3. Development Speed and Time-to-Market
Speed matters, especially for startups and fast-moving teams.
React Native accelerates mobile development by allowing you to share a large portion of code between iOS and Android. Instead of building two separate apps, you maintain one core codebase. That means faster launches, quicker iterations, and lower development costs.
ReactJS also enables rapid web development, but the real advantage in the ReactJS vs React Native comparison emerges when cross-platform mobile delivery is required.
4. Application Complexity and Performance Needs
Not all apps are created equal.
ReactJS works well for most web applications, especially when complexity is moderate and performance requirements are standard.
React Native, however, offers deeper access to native components. This makes it better suited for highly complex mobile apps, performance-sensitive workflows, or graphics-heavy experiences.
If your project demands advanced animations, device-level features, or intensive processing on mobile, React Native usually provides more control.
5. Ecosystem and Library Support
ReactJS benefits from a mature and massive web ecosystem. You’ll find libraries, frameworks, and tools for almost every use case, from UI kits to testing platforms.
React Native’s ecosystem is growing rapidly in the mobile space. While it may not yet match ReactJS in sheer volume, it offers strong support for mobile-focused features and continues to evolve quickly.
This ecosystem maturity is another important factor when weighing React Native and ReactJS.
6. Integration with Existing Codebases
Already using ReactJS for your web product?
Then React Native becomes even more attractive. You can reuse business logic, share components, and maintain consistent development patterns across web and mobile. This alignment reduces onboarding time and simplifies collaboration between teams.
7. Long-Term Maintainability
ReactJS is often easier to maintain for web-only applications thanks to its stable tooling and widespread developer adoption. React Native shines when maintaining cross-platform mobile apps, since updates can be applied to both iOS and Android from a single codebase.
From a long-term perspective, choosing between React Native and ReactJS is about reducing future complexity.
At the end of the day, ReactJS vs React Native isn’t about picking a winner. It’s about choosing the right tool for your platform, audience, and growth plans. ReactJS dominates the web. React Native powers mobile. Together, they form a flexible ecosystem that lets teams build faster, scale smarter, and deliver consistent user experiences.
Conclusion
Choosing between ReactJS and React Native is a strategic decision that directly impacts user adoption, scalability, and future innovation. Beyond features and platforms, the real differentiator lies in how well your application aligns with business goals, customer behavior, and long-term digital growth. That’s why having the right development partner matters as much as choosing the proper framework.
Ace Infoway brings skillful expertise across both ReactJS and React Native, helping businesses turn ideas into reliable, high-performance digital products.
From architecture planning to post-launch optimization, we build solutions that are designed to evolve with your business. Contact us to experience the best digital solutions and start your React journey.
FAQ
Which is better for startups: ReactJS or React Native?
It depends on your launch strategy. If you’re starting with a web MVP, ReactJS is ideal. If mobile-first is your goal, React Native helps you reach both iOS and Android faster, making ReactJS vs React Native a business-driven choice.
How scalable are ReactJS and React Native applications?
Both scale well when appropriately architected. ReactJS powers large web platforms, while React Native efficiently scales for growing mobile user bases. Scalability depends more on design patterns than on the ReactJS vs React Native framework choice.
Which is more cost-effective: ReactJS or React Native?
React Native often reduces costs for mobile projects because a single codebase supports multiple platforms. ReactJS remains cost-effective for web-only products. Your total budget varies based on scope when comparing ReactJS vs React Native.
Can ReactJS and React Native be used together in one project?
Absolutely. Many businesses use ReactJS for web apps and React Native for mobile, sharing business logic across both. This hybrid approach is common in modern ReactJS vs React Native implementations.
How secure are ReactJS and React Native applications?
Both rely on best practices rather than built-in security. ReactJS benefits from browser security layers, while React Native depends on mobile OS protections. Proper implementation matters more than the ReactJS vs React Native framework itself.